When I first started learning about artificial intelligence
(AI), one of the most fascinating things I came across was the concept of problem-solving
agents. At first, the term sounded super technical and a bit intimidating.
But once I broke it down, I realized it’s actually pretty straightforward—and
really powerful.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through what problem-solving
agents in artificial intelligence are, how they work, and share a few
real-life examples that even non-coders like you and me can easily understand.
What Is a Problem-Solving Agent in AI?
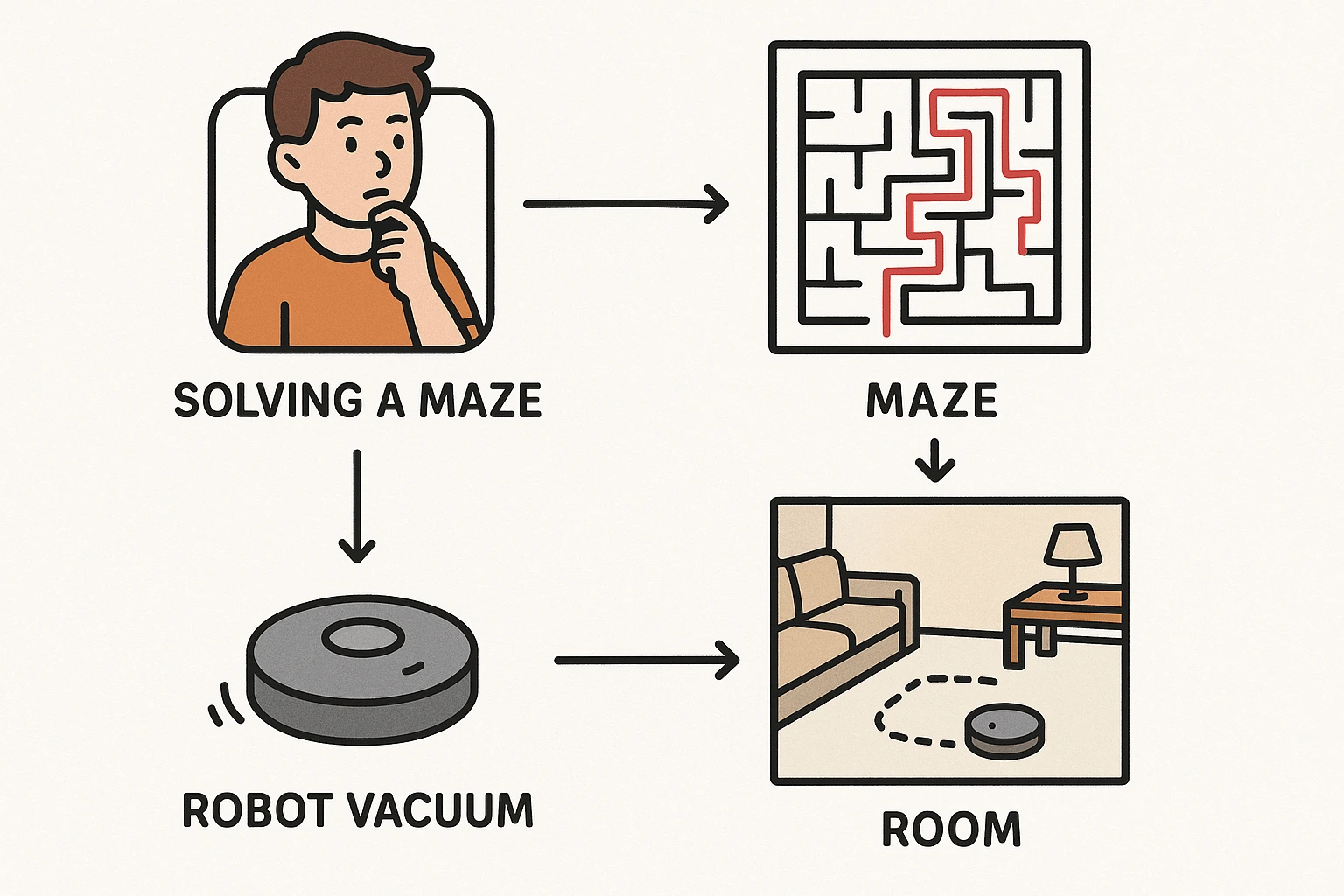
Let’s imagine you’re lost in a maze. You have to find your
way out. You don’t know the exact path, but you can see your options at each
turn and make decisions based on what you see. That’s pretty much how a problem-solving
agent works in AI.
In simple terms:
A problem-solving agent is an AI system designed to find solutions to specific problems by thinking through different possibilities and choosing the best path to reach its goal.
It works by:
- Understanding
the problem
- Exploring
possible actions (like trying different paths)
- Choosing
the best solution based on logic or rules
And the best part? It doesn’t need to be a robot. It could
be a software tool or algorithm running on a computer.
Core Components of a Problem-Solving Agent
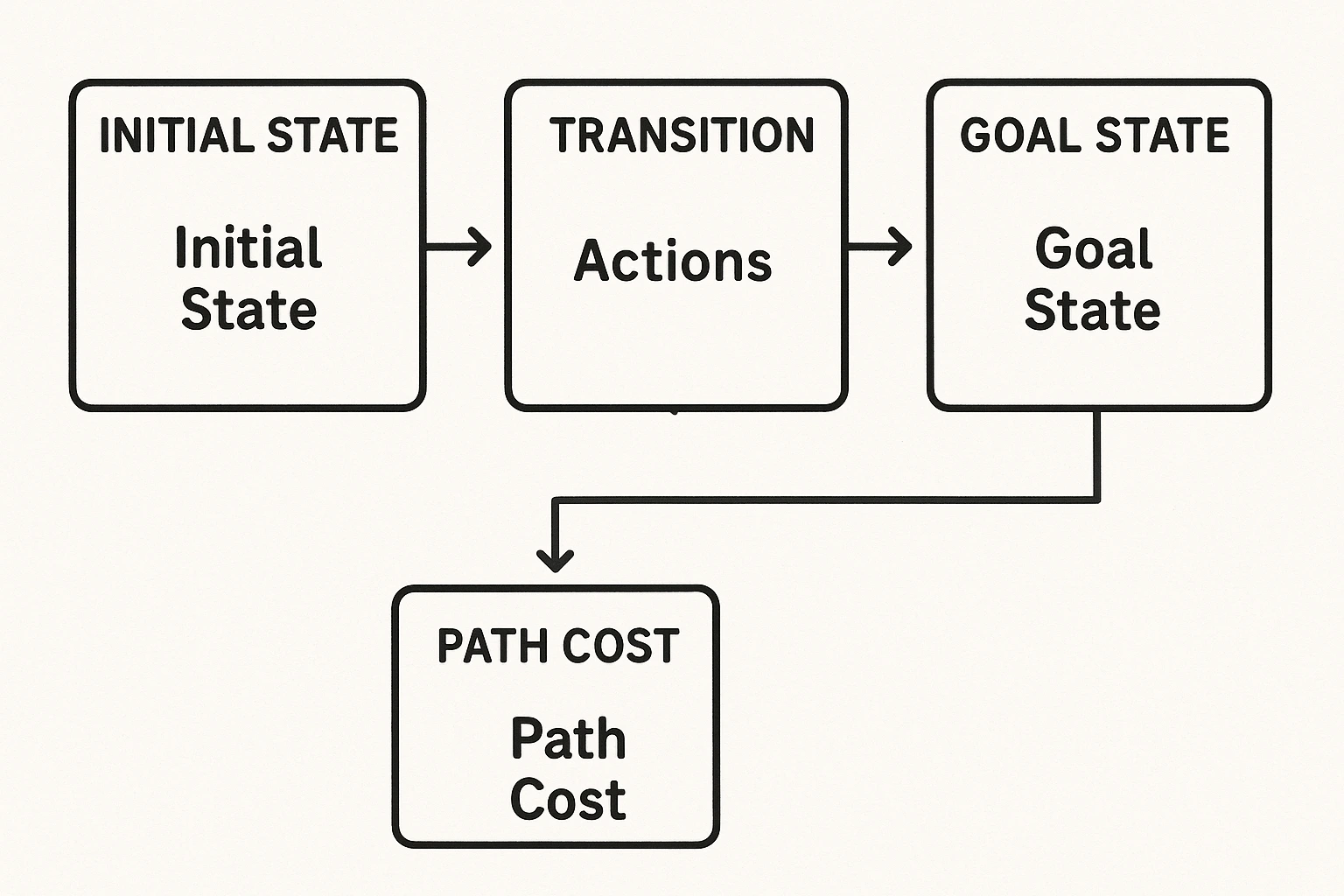
Let me break down the key parts that make up any
problem-solving agent:
1. Initial State
This is where the agent starts.
Example: You’re at home and want to reach the grocery store.
2. Actions
The different steps the agent can take to move closer to the
goal.
Example: Turn left, go straight, take the bus, etc.
3. Transition Model
This tells the agent what the result of each action will be.
Example: If you take a left, you’ll reach the traffic signal.
4. Goal State
This is what the agent is trying to achieve.
Example: Reaching the grocery store.
5. Path Cost
Sometimes, there’s more than one way to reach the goal. The path cost helps the agent choose the best route—like the shortest, cheapest, or fastest path.
How Does It Actually Work?
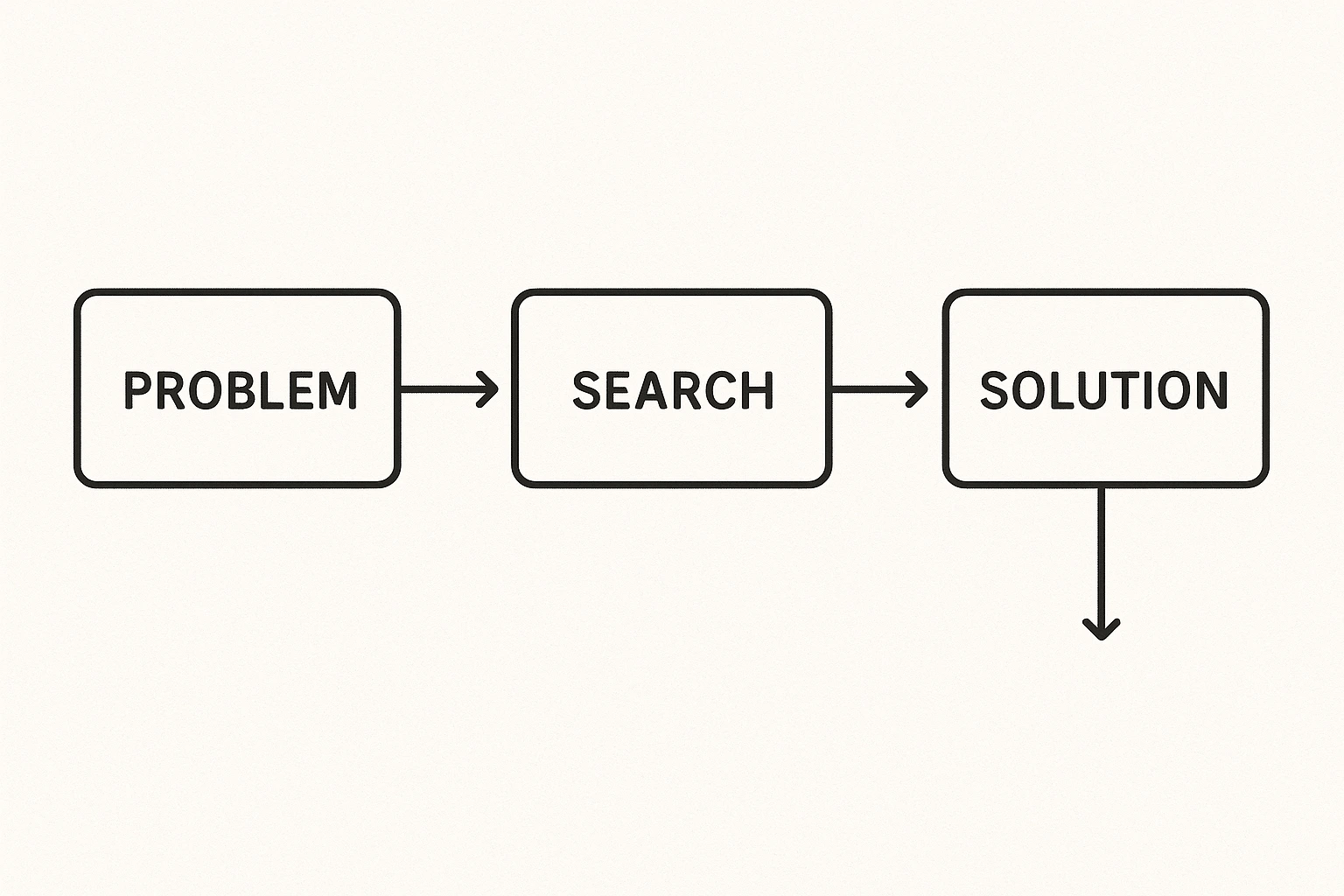
Let me break it down into easy steps. A problem-solving
agent goes through these stages:
1. Formulating the Problem
This is like asking: What’s the challenge?
For example, if the goal is to get from your house to a friend’s house using
the shortest route, the agent needs to know:
- Where
you are (start state)
- Where
you want to go (goal state)
- What
roads or paths are available (actions)
2. Searching for Solutions
This is where the agent “thinks” through different paths or
choices. It may try a few options, one at a time, or look at many possibilities
together.
Think of it like Google Maps. When you type in a
destination, it checks all possible routes and gives you the best one based on
traffic, distance, etc.
3. Choosing the Best Path
After exploring the options, the agent picks the most
efficient or correct one and follows it. It might aim to be:
- Fastest
(least time)
- Cheapest
(least cost)
- Shortest
(least distance)
The goal is to reach the target in the best way possible.
Types of Problem-Solving Agents in AI
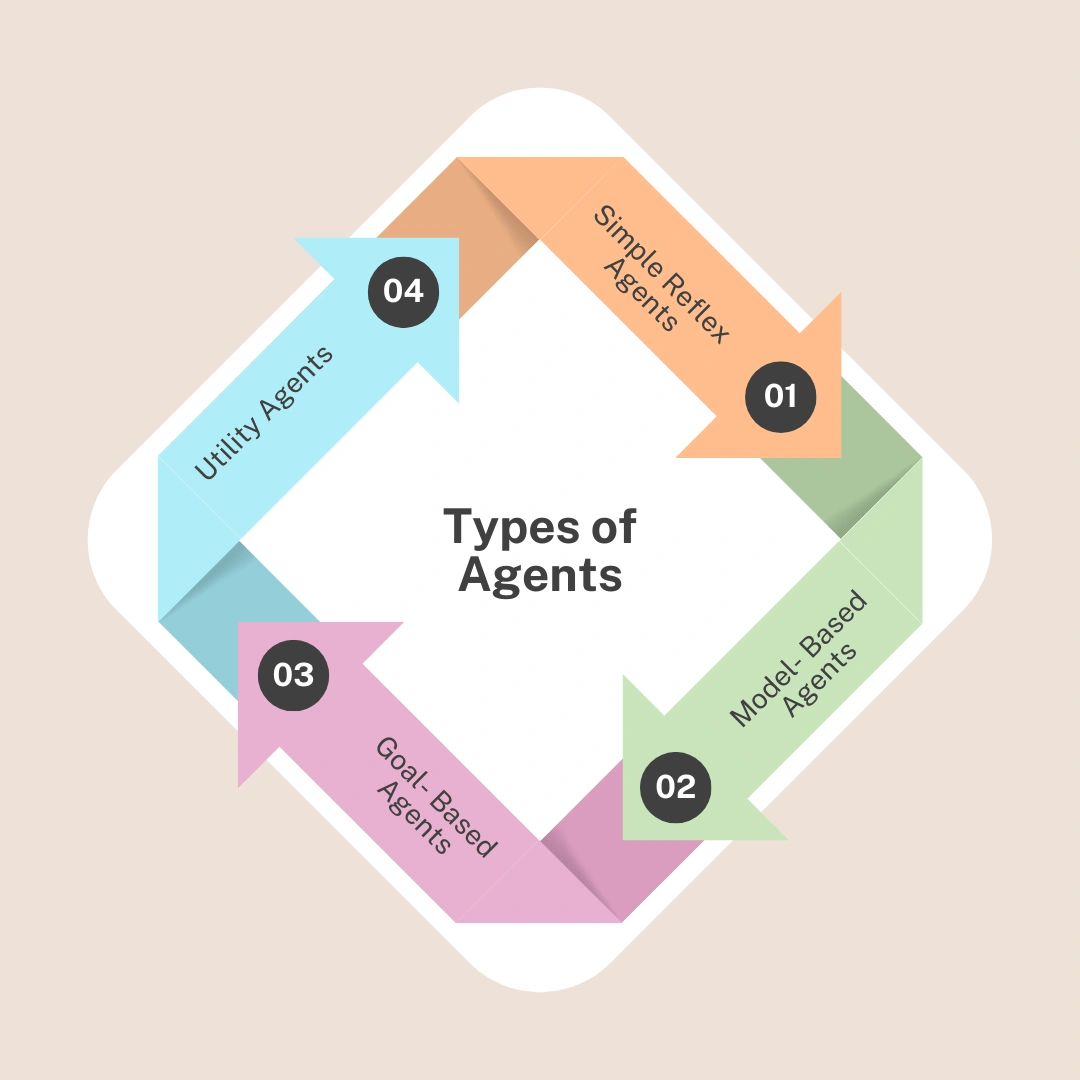
There are different kinds of problem-solving agents
depending on how smart or informed they are:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
They respond to the current situation without thinking
ahead.
Example: A light sensor that turns on a lamp when it’s dark.
2. Model-Based Agents
These agents understand how the world works and can predict
the outcome of their actions.
Example: A self-driving car that slows down when it predicts traffic ahead.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents choose actions based on achieving a specific
goal.
Example: A delivery drone planning the best path to deliver a package.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These go a step further and pick actions that not only meet
the goal but also provide the best “value” or benefit.
Example: Choosing a route that avoids traffic and also saves fuel.
Real-Life Examples (No Coding Needed!)
Here are some everyday examples of problem-solving agents
in AI that I think you'll recognize:
Google Maps or GPS Apps

When I use Google Maps, it figures out the best route for me
to get somewhere. It checks traffic, road closures, and even gives me
alternatives. This is a problem-solving agent in action—it’s solving the
problem of how to get me from point A to B.
Video Game Characters

Ever played a game where enemy characters seem to “find” you
or figure out how to block your path? That’s because those characters are using
simple AI agents to decide their next move. They have a goal (stop you or catch
you), and they explore different moves to achieve that goal.
Puzzle Solvers
Apps that solve Sudoku or Rubik’s Cubes use problem-solving
AI. They look at the puzzle, understand the current state, and then try
different combinations until they find the correct solution.
Smart Home Devices (Robot Vacuum Cleaners) (like Roomba)
.webp)
These smart vacuums move around your house, avoiding obstacles, cleaning efficiently, and figuring out where to go next. They use problem-solving logic to navigate and finish their task.
Job Application Filters
AI in HR software selects the best resumes by scanning for keywords and qualifications. It’s solving the problem of shortlisting candidates efficiently.
Why Problem-Solving Agents Matter in AI
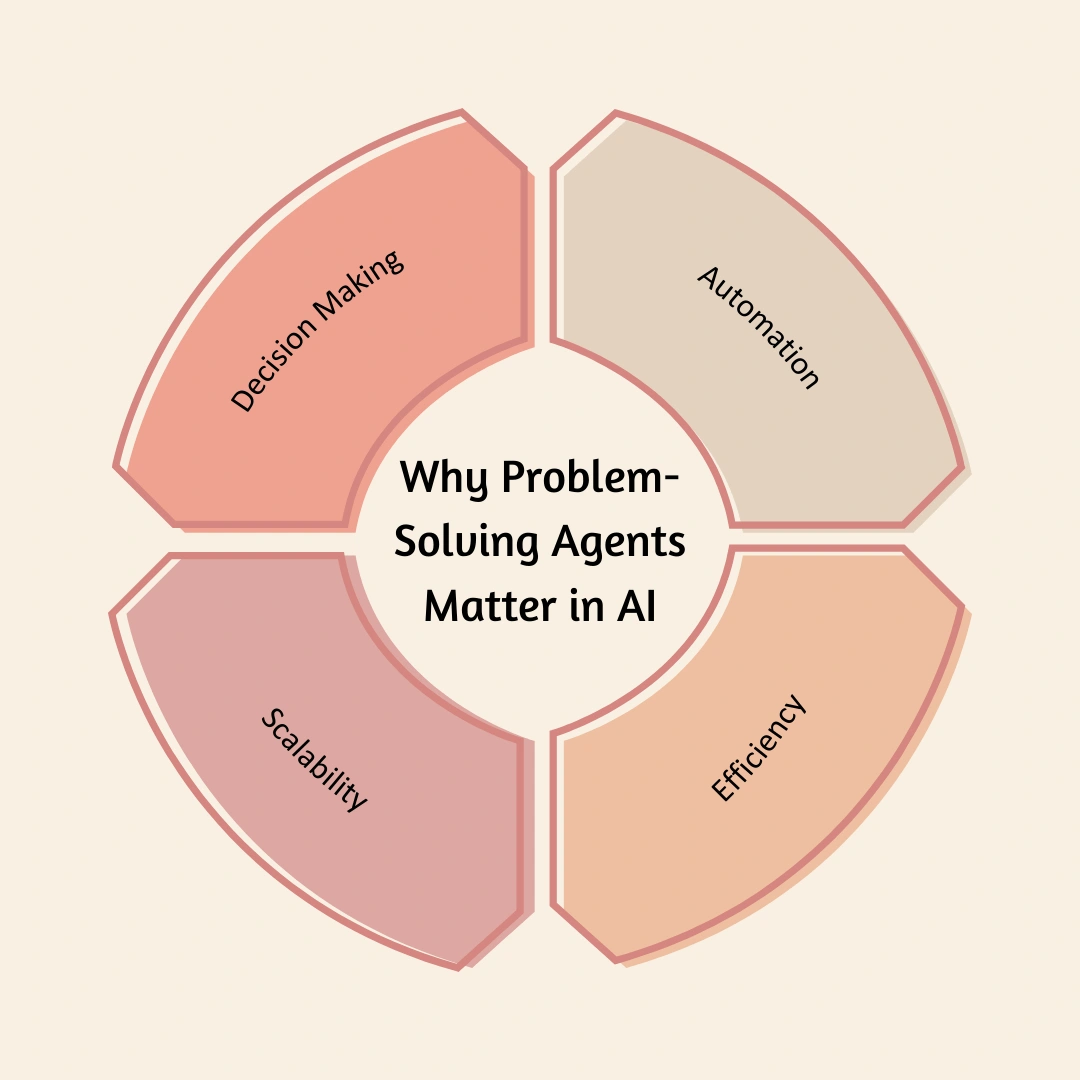
Understanding how these agents work is important because
they form the base of intelligent behavior in machines. Here’s why they
matter:
- Decision
Making: They help machines make choices without needing a human every
time.
- Automation:
They allow tools and devices to perform tasks on their own.
- Efficiency:
They optimize time, cost, and energy in reaching a goal.
- Scalability:
These agents can be used in everything from games to hospitals to space
missions.
Whether it’s a chatbot answering your questions or a drone delivering medicine, the logic behind it all starts with problem-solving agents.









Leave a Reply