If you have ever opened a website, you have seen the work of HTML. But what is HTML, exactly? This guide will explain HTML in simple words. You will learn what HTML does, how it looks, and how to write a basic page. No prior coding knowledge needed.
What is HTML?
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.
It is the language used to build web pages. Web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge read HTML files and show web pages you can see and use.
Think of HTML as the skeleton of a web page. It tells the browser what parts exist: headings, paragraphs, images, links, and lists. HTML does not decide how a page looks (color or layout). Other tools do that. HTML gives structure.
Example:
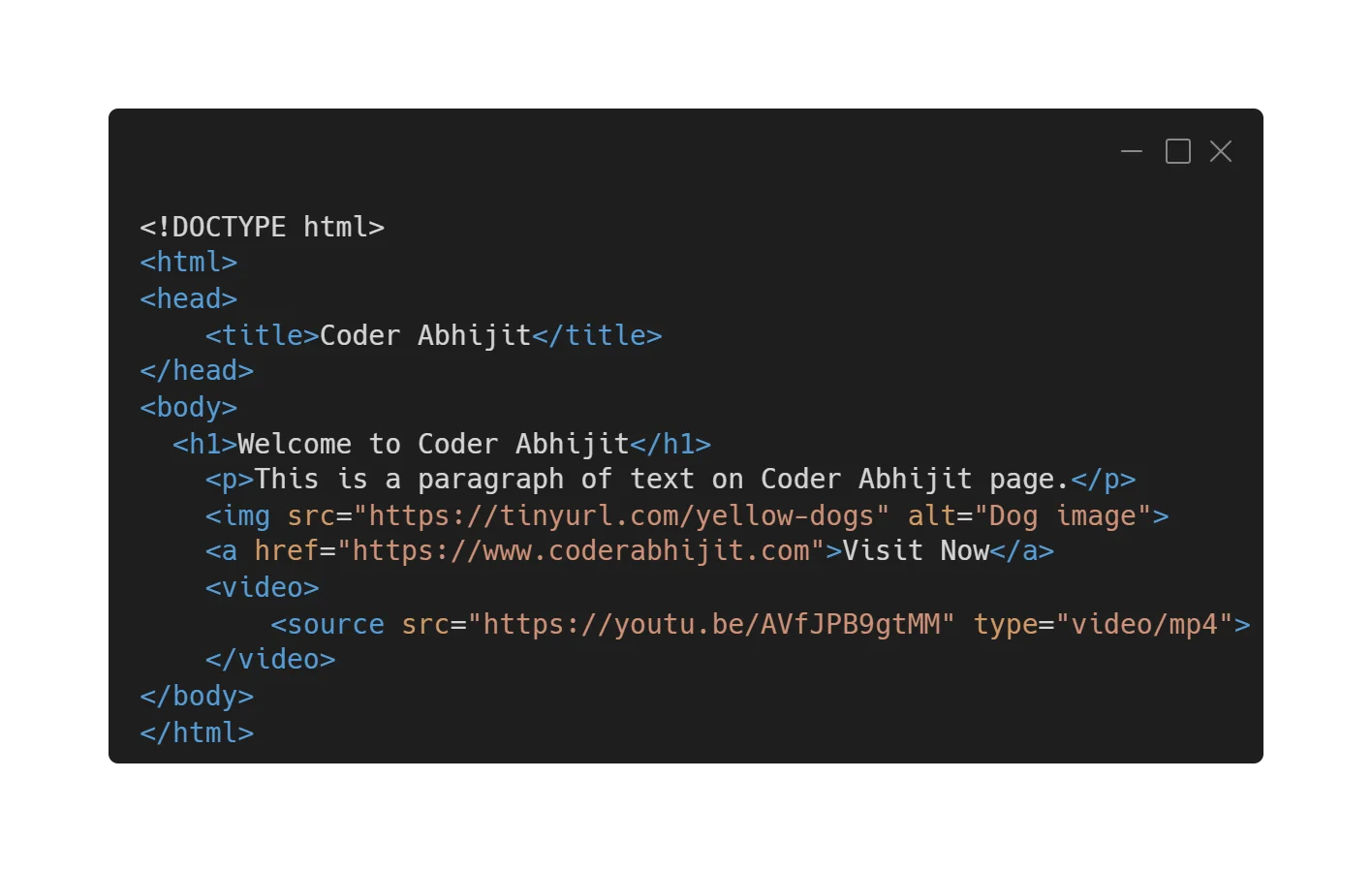
<!DOCTYPE html>tells the browser this is an HTML5 page.- <html> wraps the whole page.
- <head> holds page info, not shown on the page itself.
- <title> sets the browser tab name.
- <body> contains visible content.
- <h1> is a top-level heading.
- <p> is a paragraph.
Each element starts with an opening tag (<p>) and ends with a closing tag (</p>). Some tags do not need a closing tag; for example, the image tag <img> is self-contained and uses attributes as shown in the above image.
Common HTML elements you will use:
- <img src="" alt=""> is shows an image.
- <a href=""> for creates a link.
- <video> <source src="" type="video/mp4"> for showing the video.
Lists:
- Unordered list:
<ul><li>Item</li></ul> - Ordered list:
<ol><li>First</li></ol>
Tables: <table>, <tr>, <td> form tables.
Forms: <form>, <input>, <button> let users send data.
Each tag can have attributes. Attributes give extra information. For example, href tells a link its address.
History of HTML
HTML is an evolving language. It doesn’t stay the same for long before a revised set of standards and specifications are brought in to allow easier creation of prettier and more efficient sites.
Let’s start at the beginning...
HTML 1.0
The Hyper Text Markup Language was the brainchild of Sir Tim Berners-Lee. In 1991 he wrote a document called “HTML Tags” in which he proposed fewer than two dozen elements that could be used for writing web pages.
HTML 2.0
HTML 2.0 included everything from the original 1.0 specification but added a few new features to the mix. HTML 2.0 was the standard for website design until January 1997 and defined many core HTML features for the first time.
HTML 3.2
HTML 4.0 was recommended by the W3C in December ’97 and became the official standard in April 1998. Browser support was undertaken surprisingly earnestly by Microsoft in their Internet Explorer browser. HTML 4.0 was a large evolution of the HTML standards, and the last iteration of classic HTML.
XHTML 1.0
This is the successor to HTML. The "X" stands for Extensible. This is a reformulation of HTML 4.01 within XML (Extensible Markup Language), which is far more rigorous, and is intended to start moving the creation of Web pages away from HTML.
HTML5
HTML5 was finalized, and published, on 28 October 2014 by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). This is the fifth revision of the HTML standard since the inception of the World Wide Web.
Why HTML matters?
- HTML lets you show text and images on the web.
- It helps search engines understand your content.
- It works with CSS and JavaScript to make pages look good and behave well.
- It is the first skill to learn for web design or web development.
If you want to make a website, you must know HTML.
How a browser reads HTML
- The browser downloads an HTML file.
- It reads tags and builds a structure called the DOM (Document Object Model).
- The browser shows that structure on screen.
- If the page links to CSS, the browser applies styles. If it links to JavaScript, the browser runs scripts.
This processing happens very fast. That is why pages show almost instantly.
Advantages of HTML
- Easy to use
- Loose syntax (although, being too flexible will not comply with standards)
- Supported on almost every browser.
- Widely used; established on almost every website.
- Very similar to XML syntax, which is increasingly used for data storage
- Free - You need not buy any software
- Easy to learn & code even for novice programmers.
Disadvantages of HTML
- It cannot produce dynamic output alone, since it is a static language.
- Security features offered by HTML are limited.
- Sometimes, the structuring of HTML documents is hard to grasp.
How to start learning HTML?
- Open a plain text editor (Notepad, VS Code).
- Write the sample HTML above.
- Save as index.html.
- Double-click the file to open it in a browser.
- Change text and save. Refresh the browser to see updates.
Practice by making small pages. Try adding images, links, and lists. Small steps build skill.
Tips for writing good HTML
- Keep your code organized.
- Use indentation.
- Use meaningful names for file and image names.
- Test pages in multiple browsers.
- Use semantic elements for clarity.
- Add alt text to every image.
- Keep content simple and clear.
How HTML fits into a web project
A simple site may use:
- HTML for content
- CSS for style
- JavaScript for behavior
- Server code (like PHP) to handle data
A large site might use templates. Templates let you reuse code. But the basis remains HTML.
Common mistakes to avoid
Skipping
alttext for images.Misordered headings (
<h3>before<h2>).Forgetting to close tags.
Using HTML for layout only (use CSS for layout).
Writing long lines of code without breaks.
Fix these early. They make your pages easier to maintain.
Real-world uses of HTML
- Blog posts and news sites
- School project pages
- Portfolios and resumes
- Simple web apps interface
- Email newsletters (basic HTML)
Knowing HTML lets you make these with control and care.
FAQs About HTML
Q: What is HTML in simple words?
A: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the basic language used to create web pages. It tells a browser what to display — such as text, images, or links — using special tags.
Q: Why is HTML important?
A: HTML is important because it forms the structure of every website. Without HTML, browsers wouldn’t know how to organize or show web content. It’s the first step in learning web development.
Q: Who invented HTML?
A: HTML was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991. He developed it to share information easily between computers on the early World Wide Web.
Q: Is HTML a programming language?
A: No, HTML is not a programming language. It’s a markup language, meaning it defines the structure of content but does not perform actions or logic like a programming language does.
Q: What are HTML tags?
A: HTML tags are special codes written inside angle brackets (< >). They mark the start and end of elements like headings, paragraphs, or images. Example:
This is a paragraph.
Q: Can I make a website using only HTML?
A: Yes, but it will look plain. To make it attractive and interactive, you also need CSS (for design) and JavaScript (for actions and effects).
Q: What is the difference between HTML and HTML5?
A: HTML5 is the latest version of HTML. It adds new features.
Q: Is HTML easy to learn for beginners?
A: Yes, HTML is one of the easiest computer languages to learn. It uses simple English-like tags and requires no prior coding experience.
Q: How does HTML work in a browser?
A: When you open a web page, your browser reads the HTML code, understands the tags, and then displays the content (text, images, links) on your screen in a structured way.
Q: What software do I need to write HTML?
A: You can use any text editor — like Notepad, VS Code, or Sublime Text. Save your file with a .html extension and open it in a web browser to see the result.
Q: How long does it take to learn HTML?
A: Most beginners can learn HTML basics in one week with regular practice. To master advanced topics like forms, tables, and semantic tags, it may take a few weeks.








Leave a Reply