You know that 2026 is coming and choosing the right display is no longer simple. When buying a new phone, TV, or laptop, you’ll often see two main types of screens — LCD and OLED. Both look sharp, but they work in very different ways. In 2026, the difference between LCD vs OLED technology is even more visible, and understanding it can help you make a smarter choice.
What Is an LCD Display?

LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display.It uses a backlight that shines through layers of liquid crystals to create images. These crystals don’t produce light themselves; they control how much light passes through each pixel.
LCDs have been around for years and are used in many budget and mid-range screens. They are reliable, durable, and often cheaper to make.
Key Features:
- Requires a backlight
- Durable and affordable
- Used widely in TVs, monitors, and budget smartphones
What Is an OLED Display?

OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode.In this type of display, every pixel produces its own light. This means OLED screens can turn off individual pixels to create perfect blacks and deeper contrast.
You’ll often find OLED in premium devices like flagship smartphones, 4K TVs, and high-end monitors.
Key Features:
- Self-emitting pixels (no backlight)
- Deep blacks and vivid colors
- Found in premium devices
LCD vs OLED: What is the Key Differences
Feature | LCD Display | OLED Display |
Light Source | Uses backlight | Self-emitting pixels |
Black Levels | Dark gray blacks | True, deep blacks |
Brightness | Often brighter in sunlight | Lower peak brightness |
Color Accuracy | Decent but limited | Excellent and vivid |
Viewing Angle | Narrower | Wider, consistent colors |
Burn-in Risk | None | Possible with static images |
Power Efficiency | Uses more power for dark scenes | Saves power in dark mode |
Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Lifespan | Longer overall | Shorter in some cases |
Flexibility | Rigid screens | Can be flexible or foldable |
--------------- Don’t Miss: ----------------
 Is your Gmail full of unwanted emails? This feature offers a permanent fix give it a try today.
Is your Gmail full of unwanted emails? This feature offers a permanent fix give it a try today.
How Do They Work?
Now, we will know how LCD and OLED works.
How LCD Works
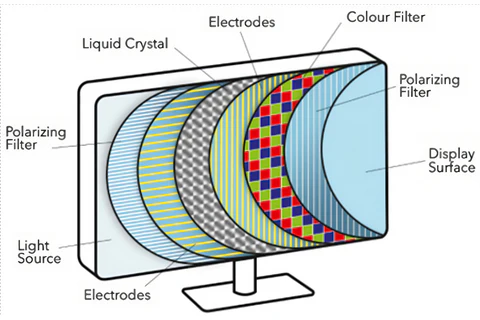
Image Credit: robocraze.com
LCD panels use several layers a backlight, polarizers, and liquid crystals to control how much light reaches your eyes. The light is always on, even when displaying black, which is why true black is hard to achieve.
How OLED Works
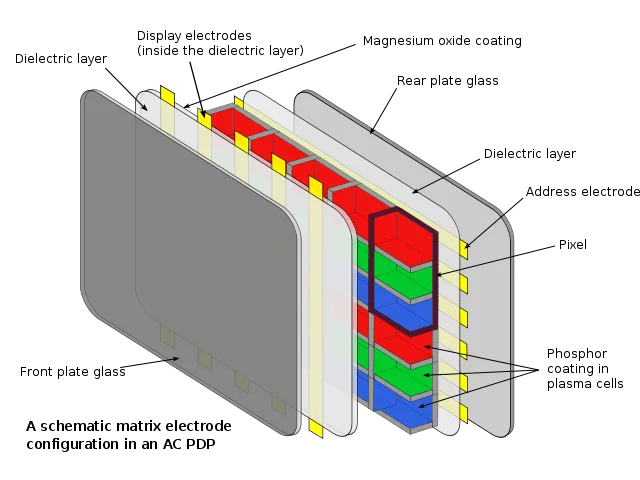
In OLED panels, each pixel acts as its own light source. When a pixel is off, it’s completely black. This gives OLED displays their famous contrast ratio and color depth.
Picture Quality: LCD vs OLED
When it comes to picture quality, OLED takes the lead. OLED screens display deeper blacks, better contrast, and more vibrant colors. The difference is especially noticeable when watching movies or playing games with dark scenes.
LCD screens, on the other hand, sometimes look washed out or have light bleeding from the edges.
Brightness and Outdoor Visibility
If you use your device mostly outdoors, LCD can still be better. LCD displays often reach higher brightness levels, making them easier to see in direct sunlight. OLED screens are improving in this area, but some models still struggle under strong light.
Power Usage
OLED displays are more power-efficient when showing dark content because black pixels are off. But if your screen is mostly white like a document or website LCD can sometimes use less power. In short, it depends on how you use your device.
Viewing Angles
OLED screens offer wider viewing angles. You can look at them from the side without color shifts or brightness loss. LCD screens may look dimmer or change color when viewed from different angles.
Durability and Burn-In
Burn-in happens when a static image (like a logo) stays on the screen for too long and leaves a faint mark. OLED screens are more likely to experience this, though new technologies have reduced the risk.
LCD screens don’t suffer from burn-in, which makes them better for long static displays — like PC monitors used for work.
Cost and Availability
In 2026, LCD displays remain cheaper to produce and buy. You’ll find them in budget TVs, monitors, and mid-range phones. OLED displays are becoming more common and affordable, but they still cost more due to complex manufacturing.
Lifespan and Maintenance
LCD panels generally last longer because the backlight degrades slowly. OLED panels may lose brightness over time, especially if used at high brightness levels. However, most users won’t notice this for several years.
Flexibility and Design Possibilities
OLED technology allows for flexible and foldable screens. That’s why modern foldable phones and rollable TVs use OLED. LCD panels are rigid, which limits creative designs.
Response Time and Gaming Performance
Gamers prefer OLED displays for their fast response times and near-instant pixel changes. This reduces motion blur and input lag. LCDs can still be good for gaming, but OLED offers a smoother, more immersive experience.
Eye Comfort
OLED displays often cause less eye strain because they emit less blue light and flicker less. Many OLED screens now include built-in eye protection features. LCD screens can be slightly harsher in low light due to constant backlighting.
HDR and Color Accuracy
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content looks best on OLED because it handles deep blacks and bright highlights better.
LCDs support HDR too, but they rely on local dimming, which can cause blooming — bright halos around dark areas.
--------------- Don’t Miss: ----------------
 By 2030, These 4 Technologies Might Completely Disappear! These are massively used by people today
By 2030, These 4 Technologies Might Completely Disappear! These are massively used by people today
Which Is Better for Phones?
For smartphones, OLED is usually the better choice. It delivers sharper visuals, true blacks, and excellent contrast while being thinner and lighter. Most flagship phones in 2026 use OLED or AMOLED (a type of OLED).
Which Is Better for TVs?
For home entertainment, OLED TVs give a cinema-like experience with rich contrast and wide viewing angles. However, LCD TVs with LED or Mini-LED backlighting are still popular for brighter rooms and lower budgets.
Which Is Better for Monitors?
If you use your monitor for work or spreadsheets, LCD may be safer because it avoids burn-in. But if you’re into video editing, design, or gaming, OLED offers unmatched color accuracy and speed.
Future of Displays in 2026 and Beyond
The line between LCD vs OLED is getting thinner. New Mini-LED and Micro-LED technologies are pushing LCDs closer to OLED-like quality, while OLED panels are becoming brighter and more durable. In the near future, you may not have to choose — hybrid screens could offer the best of both.
LCD vs OLED: Best Choice for Your Needs in 2026
LCD vs OLED which will be the best choice in 2026 according to your use perpose.
Choose LCD If You:
- Need a display for bright rooms or outdoor use
- Want a budget-friendly option
- Use your device for text, spreadsheets, or office work
- Keep screens on for long periods (like desktop monitors)
Choose OLED If You:
- Watch movies or play games often
- Prefer deeper contrast and true blacks
- Want thin, modern designs
- Use dark mode regularly to save power
In short or one word which will be the best according to price, picture quality, durability, brightness and more.
Category | Best Choice |
Picture Quality | OLED |
Brightness | LCD |
Durability | LCD |
Power Efficiency | OLED |
Price | LCD |
Gaming & Movies | OLED |
Work Use | LCD |
Conclusion
Both LCD and OLED have their strengths in 2026. If you value deep blacks, vivid colors, and modern design, OLED is the better display. If you need affordability, durability, and brightness for daily use, LCD still performs well.
When choosing between LCD vs OLED, think about how and where you’ll use your device. Each display type serves a purpose and knowing their differences helps you make the right decision.









Leave a Reply